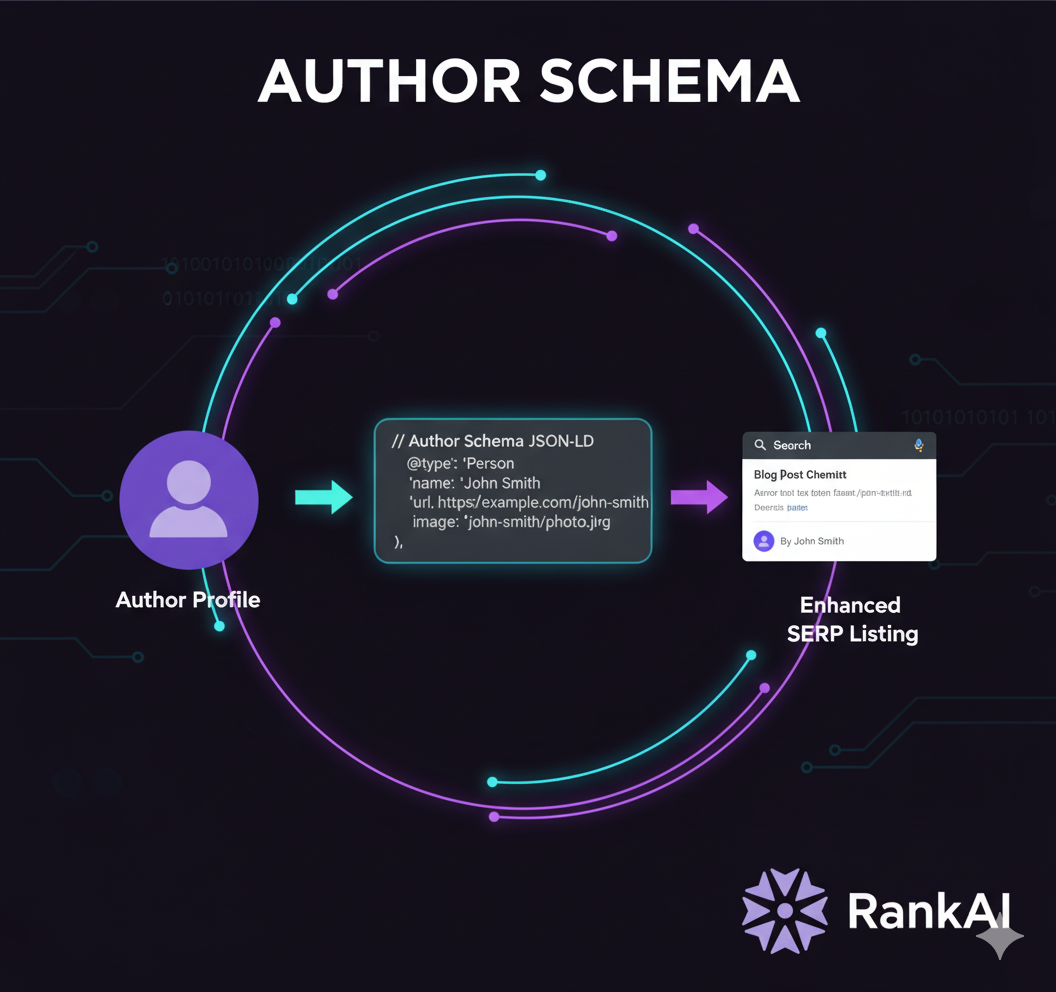
In the crowded world of online content, trust is everything. How do you signal to search engines and readers that your articles are written by credible experts? The answer often lies in a powerful piece of code called author schema.
Think of it as a digital nametag for your content. It's a specific type of structured data that explicitly tells search engines like Google who wrote a piece of content. By embedding this information directly into your webpage's code, you eliminate ambiguity and help search engines connect your content to a real person or organization, boosting its perceived authority. This is a crucial step in building a trustworthy online presence.
What Exactly Is Author Schema?
Author schema is a standardized format for providing information about a content creator. This data is usually included within a broader `Article`, `BlogPosting`, or `NewsArticle` schema. Google even lists the author property as a recommended field for articles, underscoring its importance.
This structured data typically includes key details like:
- The author's name.
- A link to their biography or profile page.
- Their professional title or role.
- Sometimes even an image or social media links for richer context.
When implemented correctly, this information can help your content qualify for rich snippets in search results. For example, Google might display the author's name directly in the search listing, giving users more confidence in the source before they even click. With rich results now appearing in roughly a third of all Google searches, leveraging author schema can give your content a significant visual edge. To ensure your markup works hand in hand with title tags, headings, and meta descriptions, follow our on-page SEO checklist.
Why Author Schema Is a Game Changer for Your SEO
Adding author schema markup isn't just a technical exercise; it delivers tangible benefits that align directly with modern SEO best practices.
Build Credibility and Trust
By clearly identifying the author, you showcase the expertise behind your content. This directly supports your site's signals for Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (often called E E A T). Google's own Quality Rater Guidelines instruct evaluators to consider the authoritativeness of the content creator when assessing page quality. A well defined author schema reinforces this trust signal for both search engines and human users.
Improve Search Visibility and Click Through Rate
Pages with structured data are often eligible for enhanced search features that make them stand out. These eye catching results naturally attract more clicks. In fact, studies have shown that websites implementing schema markup can see an average 30% increase in their click through rate (CTR) compared to those without it. When a user sees a credible author's name next to a search result, they are more likely to choose that link, especially for topics where expertise is vital. You can track CTR and rich‑result performance with these SEO reporting tools.
Establish Clear Authority for Google
The web is full of people with the same name. Author schema helps Google distinguish between them. For instance, it allows the search engine to understand that Dr. Jane Smith the cardiologist is different from Jane Smith the travel blogger. By providing a unique URL for the author, you help Google connect the dots and build a clearer picture of their expertise, which can feed into its Knowledge Graph. This process of disambiguation is critical for establishing an author's authority on specific subjects.
The Key Components of Author Schema Markup
Implementing author schema involves a few core properties. If you're diagnosing issues with structured data at scale, start with a technical SEO audit. Getting these right is essential for the markup to work correctly.
The "author" Property
This is the main container that specifies the creator of the content. According to Google's guidelines, the value for this property can be either a `Person` or an `Organization`. This flexibility means you can attribute an article to an individual writer or to your company as a whole, depending on your content strategy.
The "author.name" Property
This one is straightforward: it's a text field for the author's full name. Consistency is critical here. Experts recommend using the exact same name across all platforms, from your website's schema to the author's social media profiles. This consistency builds recognition and trust with Google's algorithms. Omitting the author's name is a critical error in structured data, so always ensure this field is filled out correctly.
The "author.url" Property
The `author.url` property provides a link to a webpage that uniquely identifies the author, such as a bio page on your site, a LinkedIn profile, or even a personal blog. This link is arguably the most powerful part of author schema because it helps Google definitively confirm the author's identity.
For best results, link to a dedicated author page on your own website. This page can showcase the author's bio, credentials, and a list of their other articles. You can even add `ProfilePage` schema to the author's bio page itself for an extra layer of clarity. Need help producing bio pages and thought leadership content? Check out these SEO content writing services.
How to Implement Author Schema (Without the Headache)
While you can write the JSON LD code by hand, several tools and services make implementing author schema much easier.
- CMS Plugins: If you use WordPress, plugins like Yoast SEO or Rank Math can automatically generate the necessary structured data. These tools draw information from your user profiles, making the process seamless. A majority of e commerce stores on WordPress already rely on these plugins for their schema needs.
- Schema Generators: Online tools can build the markup for you. You simply fill out a form with the author's details, and the tool generates a JSON LD snippet that you can copy and paste into your page's HTML. To speed this up across many pages, consider these SEO automation tools.
- Managed SEO Services: For many small businesses, technical SEO is a major pain point. The complexity and high cost of traditional agencies (often $3,000 to $10,000 per month) put proper optimization out of reach. This is where a fully managed solution shines.
A service like RankAI handles all the technical optimizations for you, including the correct implementation of author schema. Our team of experts, powered by AI, ensures your site complies with Google's latest guidelines without you ever having to touch a line of code. This hands off approach is not only convenient but also significantly more affordable, making enterprise grade SEO accessible to everyone. Curious why we recommend a modern model? See why traditional SEO agencies are bad for SMBs and how AI SEO agents change the equation.
After implementation, always use Google's Rich Results Test to validate your markup and check for errors. For day‑to‑day visibility changes, use these rank tracking tools. You can also monitor your performance in Google Search Console to see if your pages are earning rich snippets and enjoying a higher CTR.
Frequently Asked Questions About Author Schema
What is author schema in simple terms?
Author schema is a piece of code that acts like a digital nametag on your content. It clearly tells search engines like Google who wrote an article, which helps establish credibility and trust.
Is author schema a direct ranking factor?
No, simply adding author schema will not automatically boost your rankings. However, it supports trust and authority signals like E E A T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness), which are important for search quality. It also helps your content stand out in search results, which can increase clicks and engagement, indirectly influencing your performance.
Can I use an organization as the author?
Yes. The `author` property in your schema can be defined as either a `Person` or an `Organization`. This is useful for content like company announcements or reports published by the brand itself.
What's the difference between author.url and sameAs?
Both properties help identify an author. The `author.url` is typically a single link to the author's main profile page (like an on site bio). The `sameAs` property can be used to list multiple URLs that refer to the same author, such as their LinkedIn, Twitter, and Wikipedia pages. Google understands both.
Do I need author schema for every page?
You should use it for any content that has a clear author, especially blog posts, articles, and news stories. It is less relevant for product pages or your homepage unless they feature authored content. For more step‑by‑step guides on structured data and content optimization, browse the RankAI blog.
How does author schema help with E E A T?
It provides search engines with verifiable information about the creator's identity and credentials. By linking to an author's bio page that details their expertise and experience, you provide concrete evidence to support the E E A T principles, which is especially important for financial or health related topics.
What happens if I implement author schema incorrectly?
Incorrect implementation can lead to errors that prevent Google from reading your structured data. It could also make your site ineligible for rich results. At worst, providing misleading information (like an author in the code who isn't visible on the page) could violate Google's guidelines. That's why using a trusted tool or a managed service like RankAI is a safe bet.