Table of Contents
Your Ultimate Guide to Performing a Technical SEO Audit
Is your website struggling to climb the Google rankings despite great content? The culprit might be hiding in your site's technical setup. A technical SEO audit is like a health check-up for your website, ensuring search engines can find, understand, and rank your pages effectively. Don't worry, it's not as daunting as it sounds! Let's walk through how to perform a technical SEO audit step-by-step, making sure your site is in tip-top shape.

Think of technical SEO as the foundation of your house. If the foundation is shaky, it doesn't matter how beautiful the rest of the house is. Similarly, even the best content can falter without a solid technical SEO base. It's all about optimizing your website's infrastructure so search engines can easily crawl and index it. This is crucial because if Google can't properly access your site, your pages won't show up in search results, and you'll miss out on valuable traffic.
9 Steps to Perform a Technical SEO Audit
Step 1: Check Crawlability and Indexability
First things first: can search engines even find and read your website? If not, all your other SEO efforts are for nothing.

- What to do:
- Review your robots.txt file: This file tells search engine crawlers which pages or sections of your site they can or cannot access. Make sure you're not accidentally blocking important content. A common mistake is disallowing CSS or JavaScript files, which can prevent Google from rendering your pages correctly.
- Check your XML Sitemap: An XML sitemap is a list of your website's important pages that helps search engines discover and index them. Ensure it's up-to-date and submitted to Google Search Console. For e-commerce sites, this is especially important for product discoverability.
- Use Google Search Console: The Coverage Report in Google Search Console is your best friend here. It will show you if Google is having trouble indexing any of your pages and why. Look for errors like 404s (page not found) or server errors.
- Look for
noindextags: These tags tell search engines not to index a specific page. Make sure they're only used on pages you genuinely want to keep out of search results (like thin content or internal login pages). - For businesses looking to automate complex technical fixes, AI-powered technical SEO fixes offer one-click solutions for optimizing titles, meta tags, and structured data through its AI-driven approach to technical SEO.
- Why it matters: If search engines can't crawl your site efficiently or find your key pages, those pages simply won't appear in search results.
- Tools needed: Google Search Console, a website crawler like Screaming Frog.
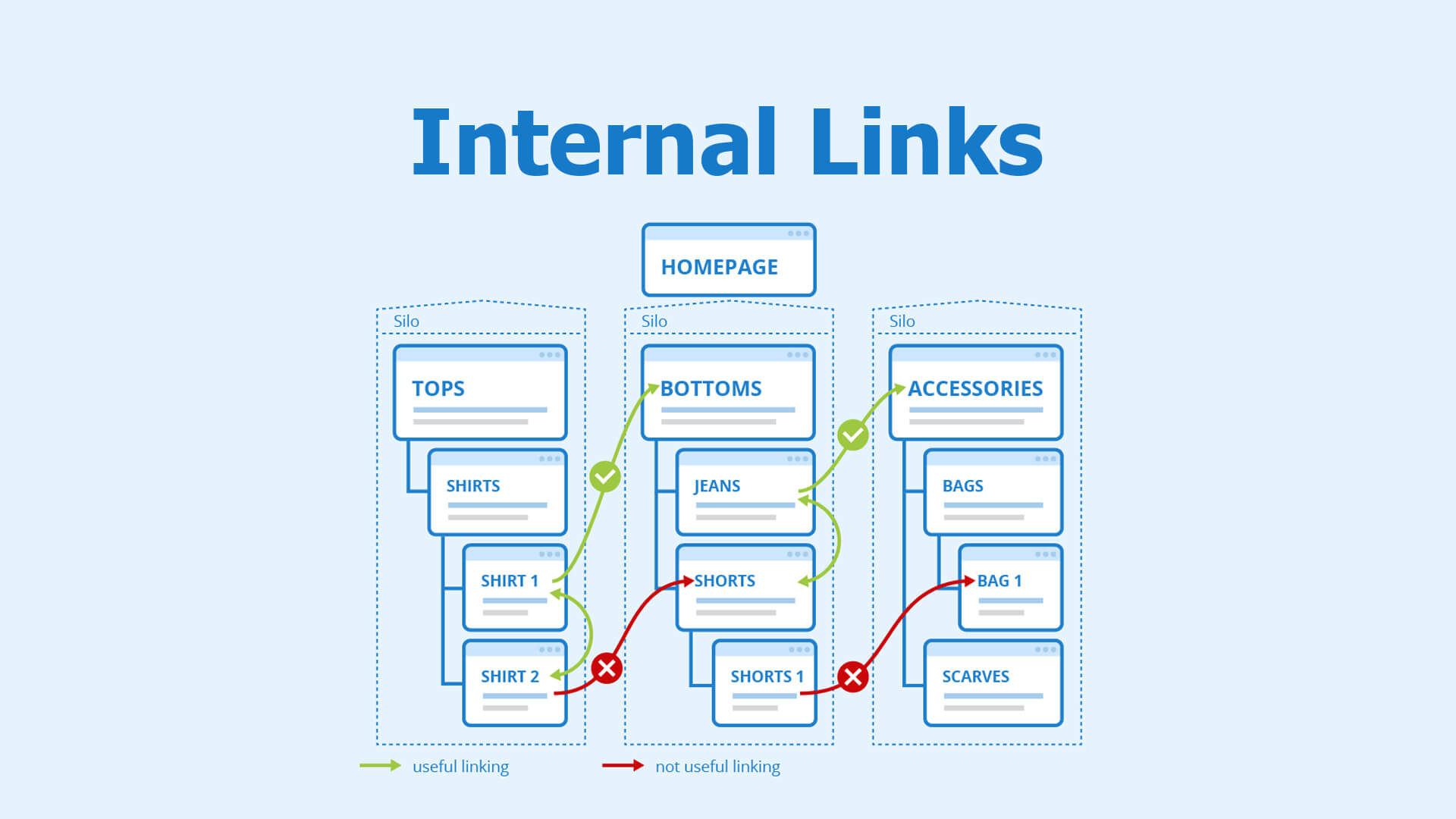
Step 2: Audit Your Site Architecture and Internal Linking
A well-organized website structure helps both users and search engines navigate your site.
- What to do:
- Aim for a logical hierarchy: Your important pages should be easy to find, ideally within 3-4 clicks from the homepage. Think of it like a well-organized filing cabinet.
- Check internal links: These are links from one page on your site to another. They help distribute link equity (ranking power) throughout your site and guide users to relevant content. Ensure your important pages have sufficient internal links pointing to them. Use descriptive anchor text for these links.
- Identify and fix orphaned pages: These are pages with no internal links pointing to them, making them hard for search engines and users to find.
- Why it matters: Good site architecture improves user experience and helps search engines understand the relationship between your pages, which can boost your rankings.
- Tools needed: Screaming Frog (for visualizing site structure and finding orphaned pages), Google Search Console.
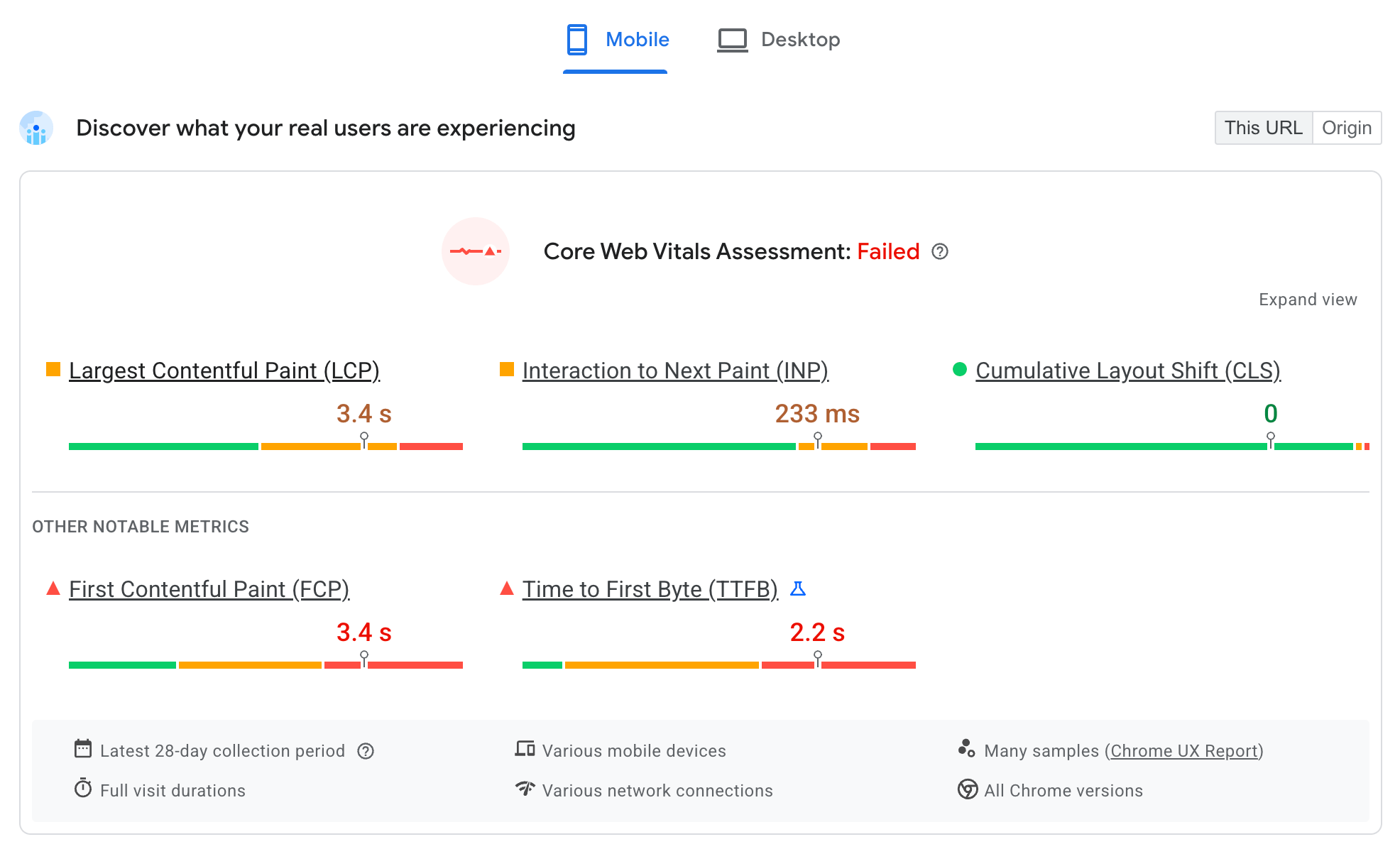
Step 3: Analyze Site Speed and Core Web Vitals
Page speed is a critical ranking factor. Slow-loading sites frustrate users and can lead to lower rankings.
- What to do:
- Test your Core Web Vitals: These are specific metrics Google uses to measure user experience, including:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): How quickly the main content of a page loads. Aim for ≤ 2.5 seconds.
- First Input Delay (FID) / Interaction to Next Paint (INP): How quickly your page responds to user interactions. Aim for FID ≤ 100 ms. (Note: INP is replacing FID as a Core Web Vital in March 2024).
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): How much your page layout unexpectedly shifts during loading. Aim for ≤ 0.1.
- When optimizing images, consider implementing modern image compression techniques like WebP which can reduce file sizes by up to 30% compared to traditional formats while maintaining quality.
- Minimize CSS and JavaScript: Remove unnecessary code or minify files.
- Enable browser caching: This allows repeat visitors to load your site faster.
- Consider server-side improvements: This might include upgrading your hosting or using a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
- Test your Core Web Vitals: These are specific metrics Google uses to measure user experience, including:
- Why it matters: Faster sites provide a better user experience, which Google rewards.
- Tools needed: Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, Google Lighthouse.
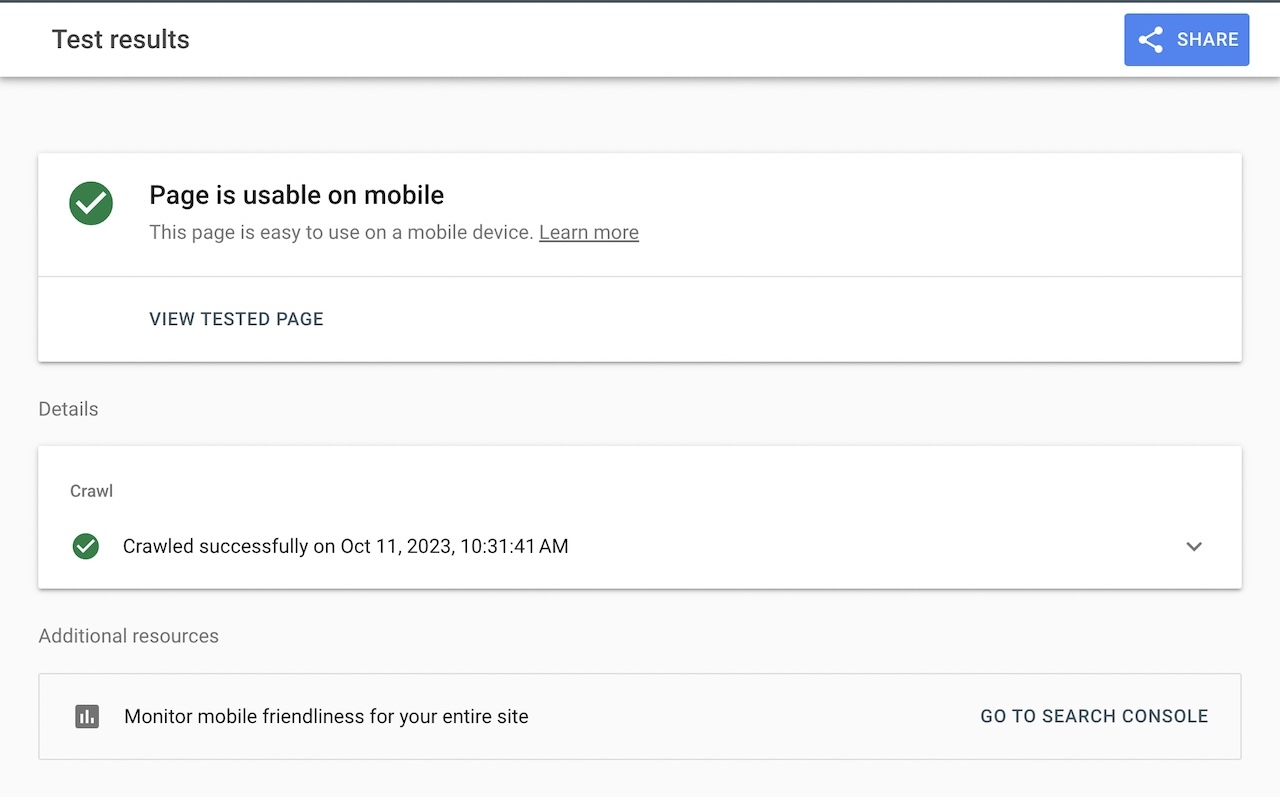
Step 4: Ensure Mobile-Friendliness
With Google's mobile-first indexing, the mobile version of your site is what Google primarily uses for ranking.
- What to do:
- Use responsive design: Your website should adapt seamlessly to different screen sizes.
- Check viewport configuration: Ensure the
meta name="viewport"tag is correctly implemented. - Test touch target sizes: Buttons and links should be large enough to tap easily on a mobile screen.
- Use Google's Mobile-Friendly Test tool.
- Review the Mobile Usability report in Google Search Console.
- When testing mobile-friendliness, pay special attention to Google's mobile-first indexing requirements, particularly regarding viewport configurations and touch target sizing.
- Why it matters: A non-mobile-friendly site will rank poorly in mobile search results and frustrate users on smartphones and tablets.
- Tools needed: Google's Mobile-Friendly Test, Google Search Console.
Step 5: Check for HTTPS and Security Issues
Security is paramount. HTTPS (secure browsing) is a confirmed ranking signal.

- What to do:
- Ensure your site uses HTTPS: This means having an SSL certificate installed.
- Force HTTPS: Redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS.
- Check for mixed content: This occurs when an HTTPS page loads some resources (like images or scripts) over an insecure HTTP connection. Fix these immediately.
- Why it matters: HTTPS protects user data and builds trust. Google prioritizes secure sites.
- Tools needed: Your browser's developer tools, SSL checker tools, Google Search Console.
Step 6: Fix Broken Links and Redirects
Broken links (404 errors) create a poor user experience and can waste crawl budget.
- What to do:
- Find and fix 404 errors: Remove internal links pointing to pages that no longer exist or redirect them to relevant live pages.
- Manage redirects correctly:
- Use 301 redirects for content that has permanently moved. This passes most link equity.
- Use 302 redirects for temporary moves (these don't pass link equity).
- Avoid redirect chains (one redirect leading to another, and another…).
- Why it matters: Fixing broken links improves user navigation and ensures search engines can efficiently crawl your site and pass link equity correctly.
- Tools needed: Screaming Frog, Ahrefs Broken Link Checker, Google Search Console.
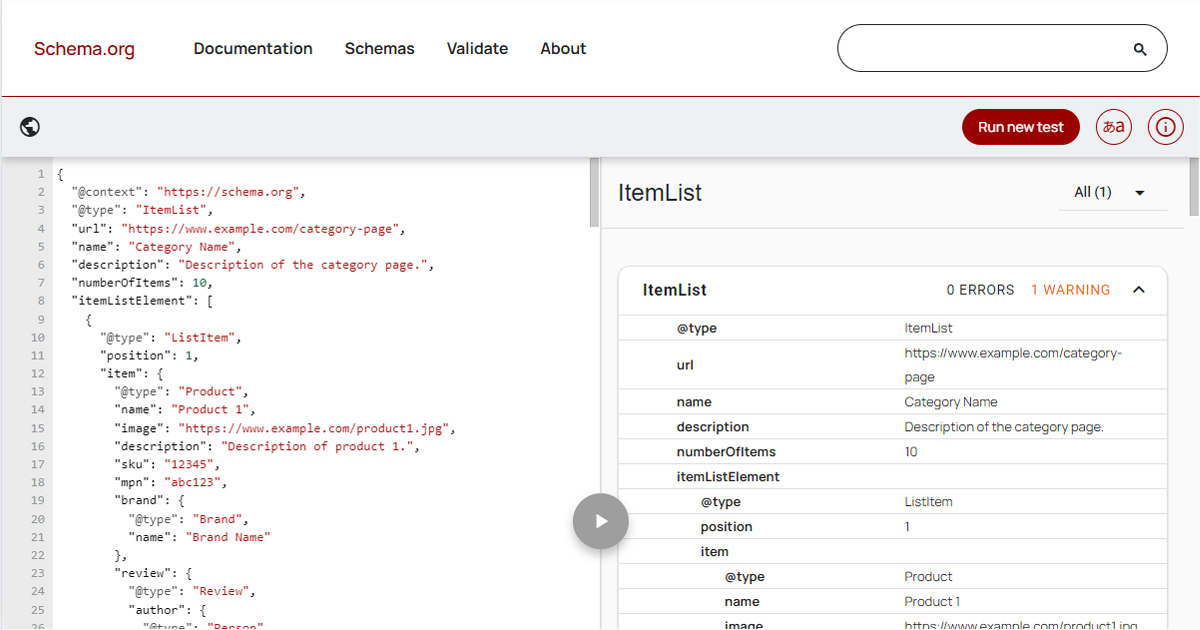
Step 7: Implement Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Structured data is code that helps search engines understand your content better, which can lead to rich snippets in search results (e.g., star ratings, FAQs, product prices).
- What to do:
- Identify opportunities for Schema Markup: Common types include Article, FAQPage, Product, LocalBusiness, and HowTo.
- For structured data implementation, automated JSON-LD markup generation enables RankAI's content intelligence system to automatically detect FAQ opportunities and generate compliant JSON-LD markup without manual coding.
- Validate your structured data using Google's Rich Results Test.
- Why it matters: Rich snippets can significantly improve your click-through rates from search results.
- Tools needed: Google's Rich Results Test, Schema Markup Validator.
Step 8: Address Duplicate Content
Duplicate content means that similar or identical content appears on multiple URLs. This can confuse search engines and dilute your ranking signals.
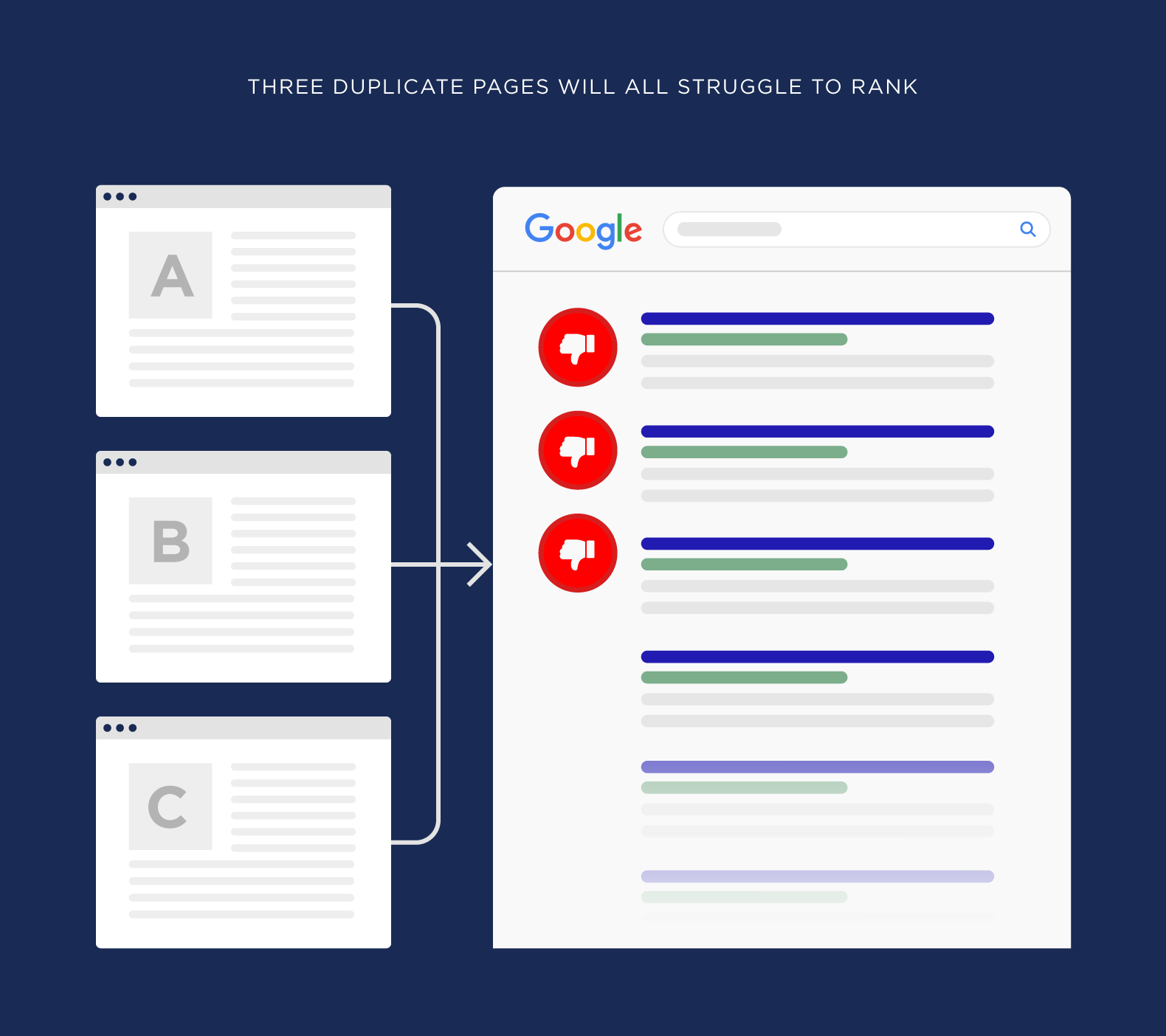
- What to do:
- Find duplicate content: Use tools like Siteliner or Semrush Site Audit.
- When resolving duplicate content issues, employ smart canonical tag implementation strategies that preserve link equity while eliminating content duplication risks.
- Use 301 redirects where appropriate (e.g., for www vs. non-www or HTTP vs. HTTPS versions of your site).
- Why it matters: Resolving duplicate content ensures that the correct pages rank and that link equity isn't split between multiple versions.
- Tools needed: Semrush Site Audit, Siteliner, Google Search Console.
Step 9: Check JavaScript Rendering (If Applicable)
If your website heavily relies on JavaScript to display content, you need to ensure search engines can render it correctly.

- What to do:
- Use Google's URL Inspection tool in Search Console to see how Googlebot renders your pages.
- Ensure critical content is not hidden behind JavaScript that search engines can't process.
- Consider dynamic rendering or server-side rendering for JavaScript-heavy sites.
- Why it matters: If Google can't see your content because of JavaScript issues, it can't rank it.
- Tools needed: Google Search Console (URL Inspection Tool).
Automate and Monitor with Rankai
Performing a manual technical SEO audit can be time-consuming, especially for larger websites or if you're managing multiple client sites. This is where AI-powered platforms like Rankai come in. Rankai can automate many of these technical checks, provide a comprehensive evaluation, and even offer one-click fixes for common issues like optimizing titles, meta descriptions, H1 tags, and alt text. It integrates with popular platforms like WordPress, Shopify, and Wix, making implementation seamless. Plus, with weekly progress reports and dashboard analytics, you can continuously monitor your site's technical health and SEO performance.

For SMBs, e-commerce stores, and startups looking to grow organically without the high costs of traditional agencies, Rankai offers an affordable, AI-driven solution to make enterprise-grade SEO accessible. Consider scheduling a demo to see how it can simplify your technical SEO efforts.
Conclusion
A thorough technical SEO audit is an essential part of any successful SEO strategy. By systematically working through these steps, you can identify and fix issues that might be holding your website back from its full potential in search engine rankings. While some aspects can be complex, many common problems have straightforward solutions. Regular audits will help keep your site healthy, fast, and easily discoverable by both users and search engines.
Remember, technical SEO isn't a one-time task but an ongoing process. As search engine algorithms evolve and your website changes, new issues can arise. By staying vigilant and proactive, you'll build a strong foundation for long-term SEO success. Rankai's comprehensive SEO dashboard provides real-time tracking of technical health metrics, crawl errors, and indexing status through intuitive visualizations.
Feeling overwhelmed by the intricacies of technical SEO audits and their ongoing maintenance? If you're looking for a way to simplify this process and ensure your website stays technically sound, discover how Rankai offers AI-powered automation for audits, one-click fixes, and continuous monitoring to make enterprise-grade SEO accessible for your business.


